Practice Basic SQL#
Start off by downloading the following files then Connect a Data Source and Upload a File.
Dummy Customers-1.xlsx
Dummy Customers-2.xlsx
Querying Data#
SELECT
This clause extracts data from a data source. A data source can be an uploaded file (xls, csv, json, etc.), or an externally connected source such as a database, cloud storage, or an API.
- To return the whole table, use a
* - To return specific columns from a table, use the column name(s)
- You can also perform simple calculations within the
SELECTclause
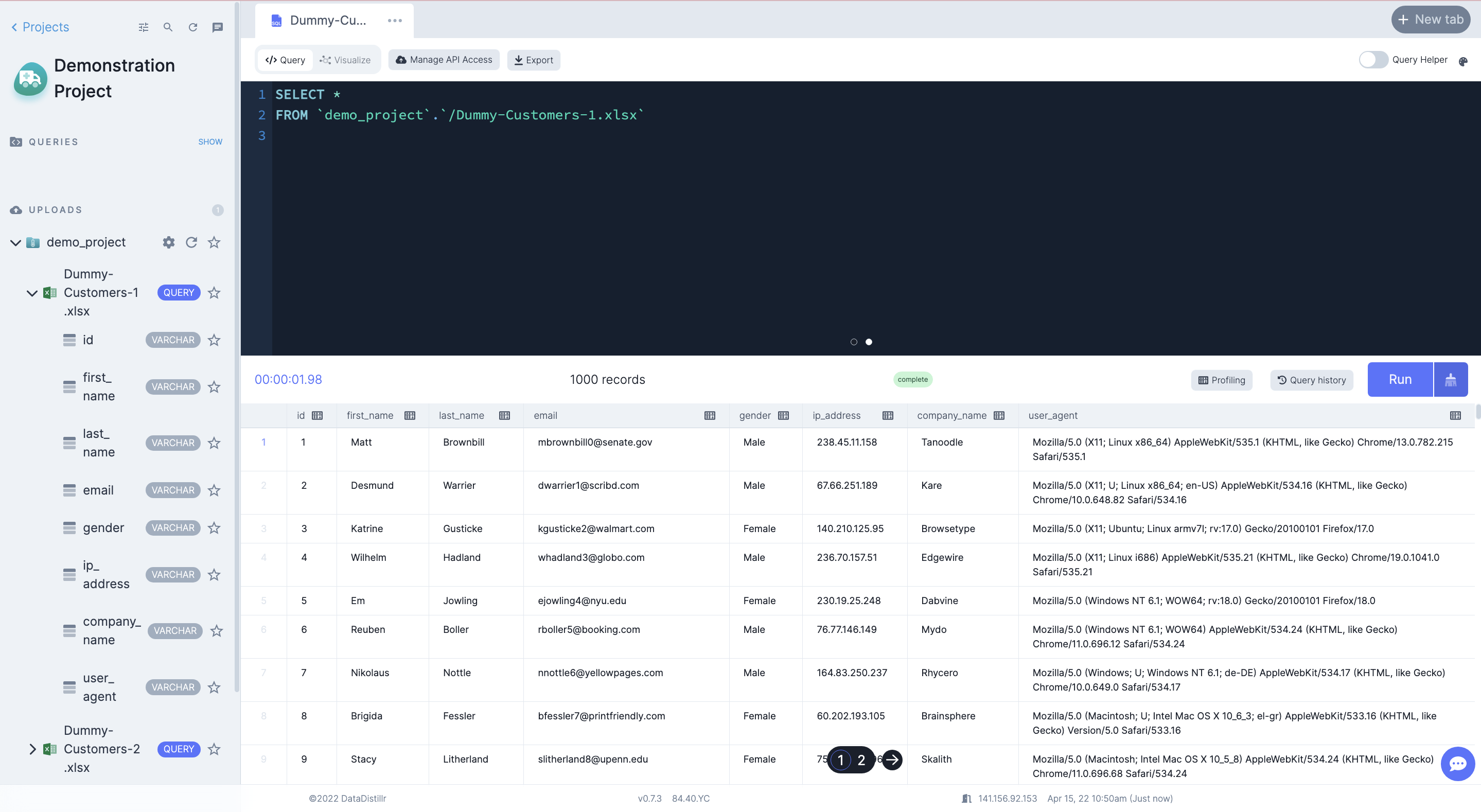
-- Display all available fields in the dataset
SELECT *
FROM `demo_project`.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
LIMIT
This clause constrains the number of rows returned by a SELECT statement.
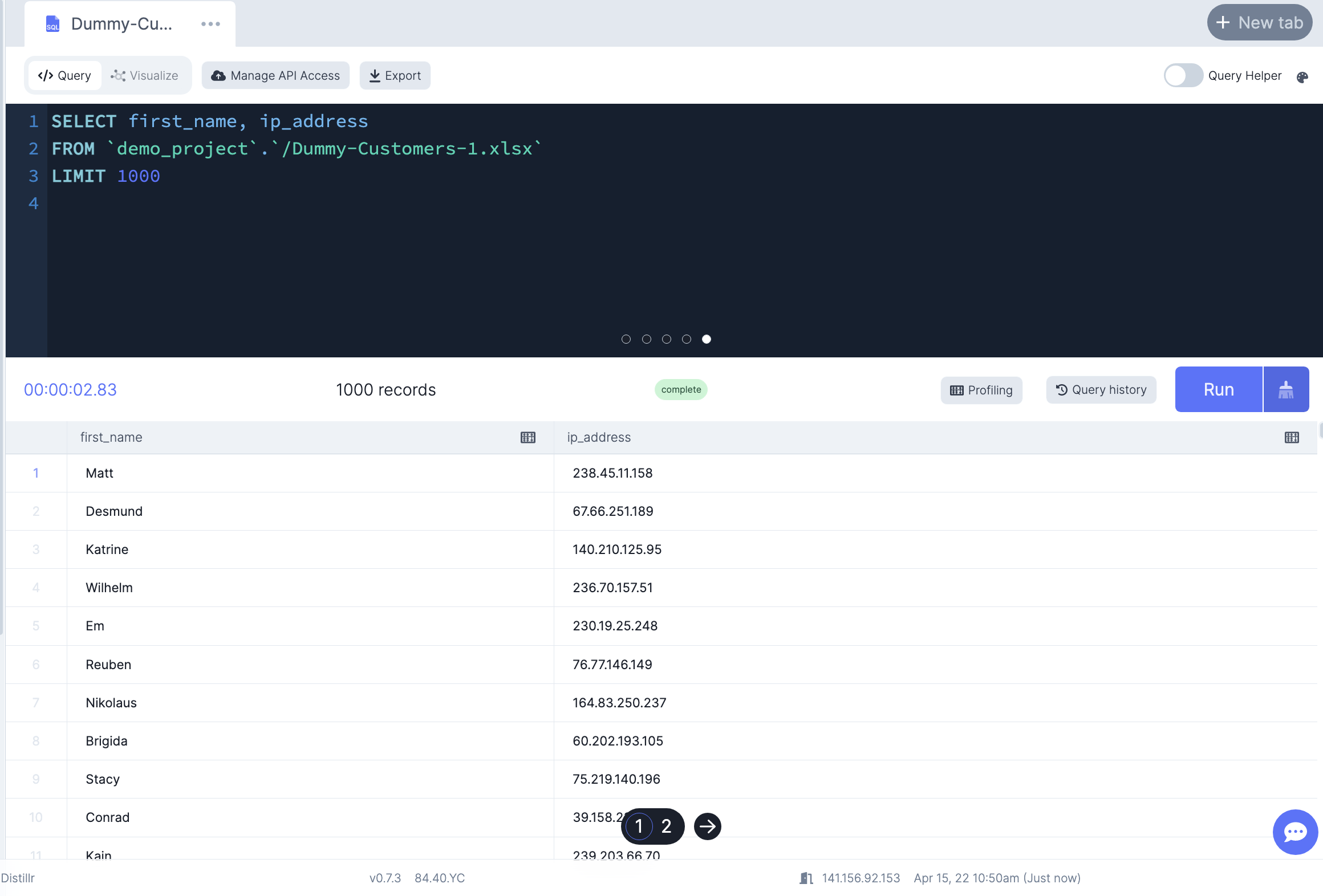
-- Display the first 1000 rows from column first_name and ip_address
SELECT first_name, ip_address
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
LIMIT 1000
Sorting Data#
ORDER BY
This clause sorts the result set based on specified criteria in ascending or descending orders.
- By default, this sorts by in ascending order. The
ASCkeyword does the same thing. - To change to descending order, add the
DESCkeyword after the column name
-- List client's first and last names in ascending order based on last name
SELECT first_name,last_name
FROM `demo_project`.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
ORDER BY last_name
Filtering Data#
SELECT DISTINCT
This clause filters out duplicate from the selected column or whole dataset and returns only unique records.
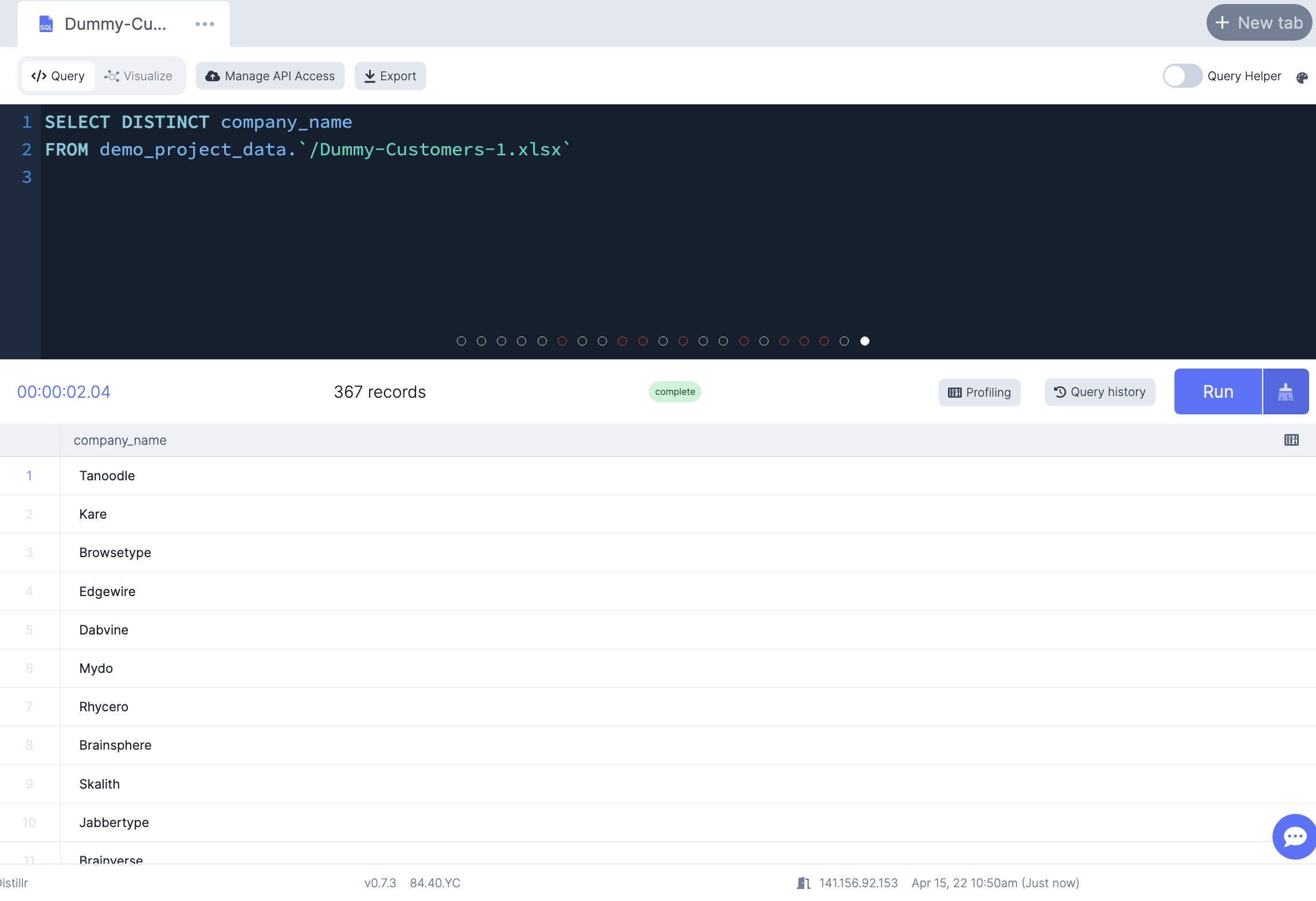
-- Select only unique company names from the company_name column
SELECT DISTINCT company_name
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
WHERE
This clause filters columns to extract only records that fulfill the specified condition.
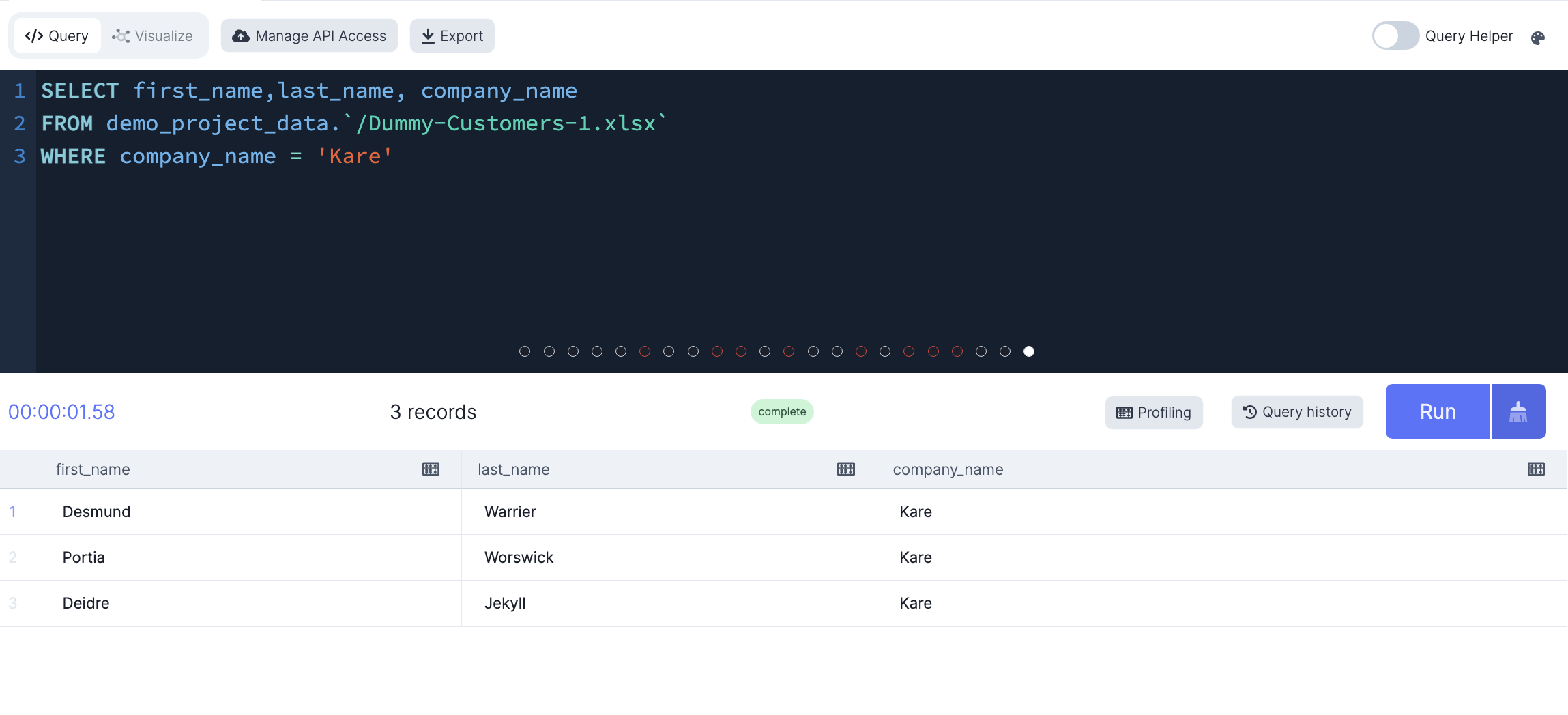
-- Only select the customers from the Kare company
SELECT first_name,last_name, company_name
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
WHERE company_name = 'Kare'
Operators#
You can use the following comparison operators to test if conditions are True or False
| Comparison Operators | Description | Usage |
|---|---|---|
| = | Equal | column = expression |
| > | Greater Than | column > expression |
| < | Less Than | column < expression |
| >= | Greater Than or Equal | column >= expression |
| <= | Less Than or Equal to | column <= expression |
| <> , != | Not Equal to | column != expression |
The WHERE clause can also be combined with the following operators detailed below:
- AND
- OR
- NOT
- IN
- BETWEEN
AND
This operator filters records based on more than one condition and displays a record if the conditions on both sides of
the AND are TRUE.
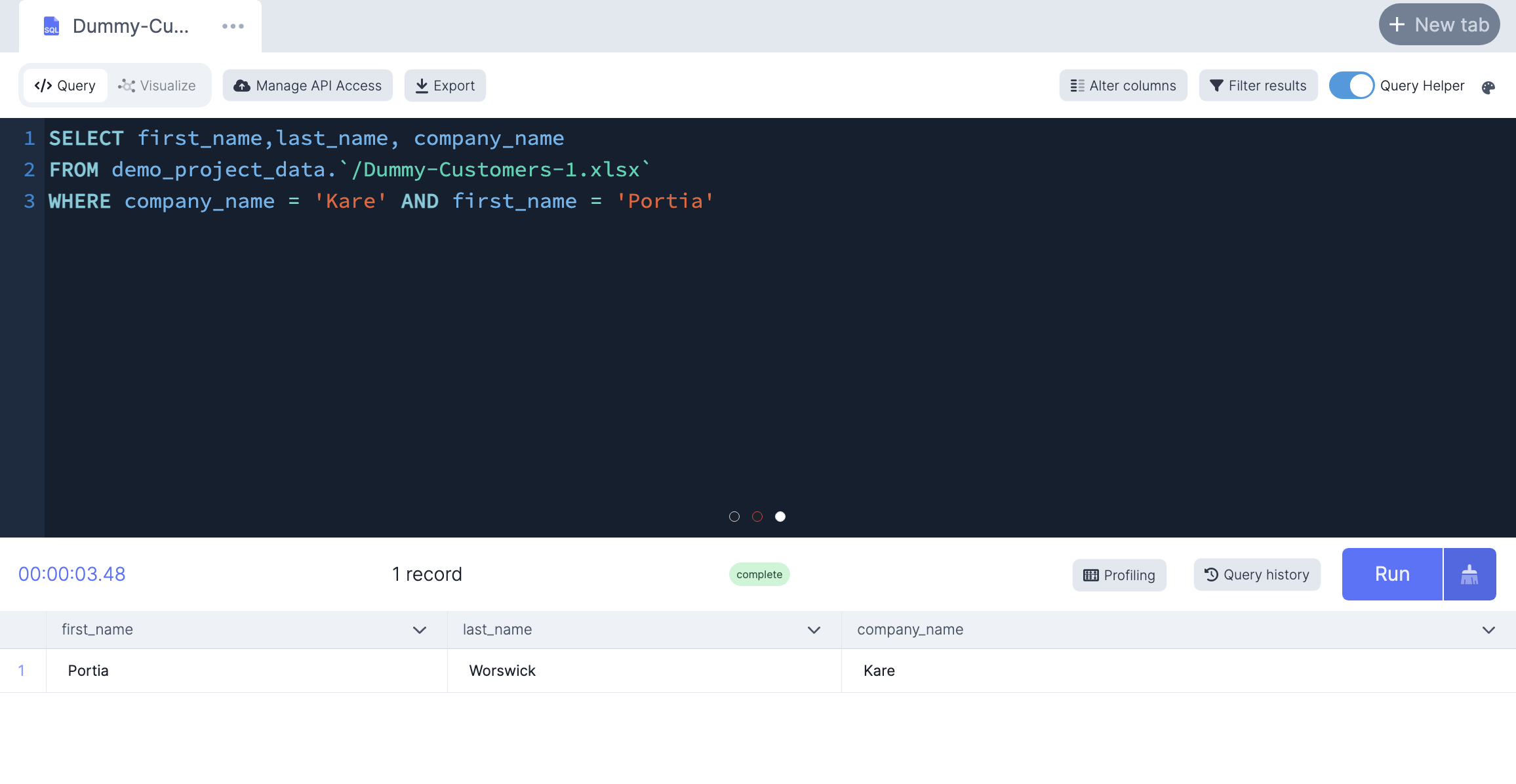
-- Only select customers from the Kare company AND whose first name is Portia
SELECT first_name,last_name, company_name
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
WHERE company_name = 'Kare' AND first_name = 'Portia'
OR
This operator filters records based on more than one condition and displays a record if any of the conditions on either
side of the OR are TRUE.
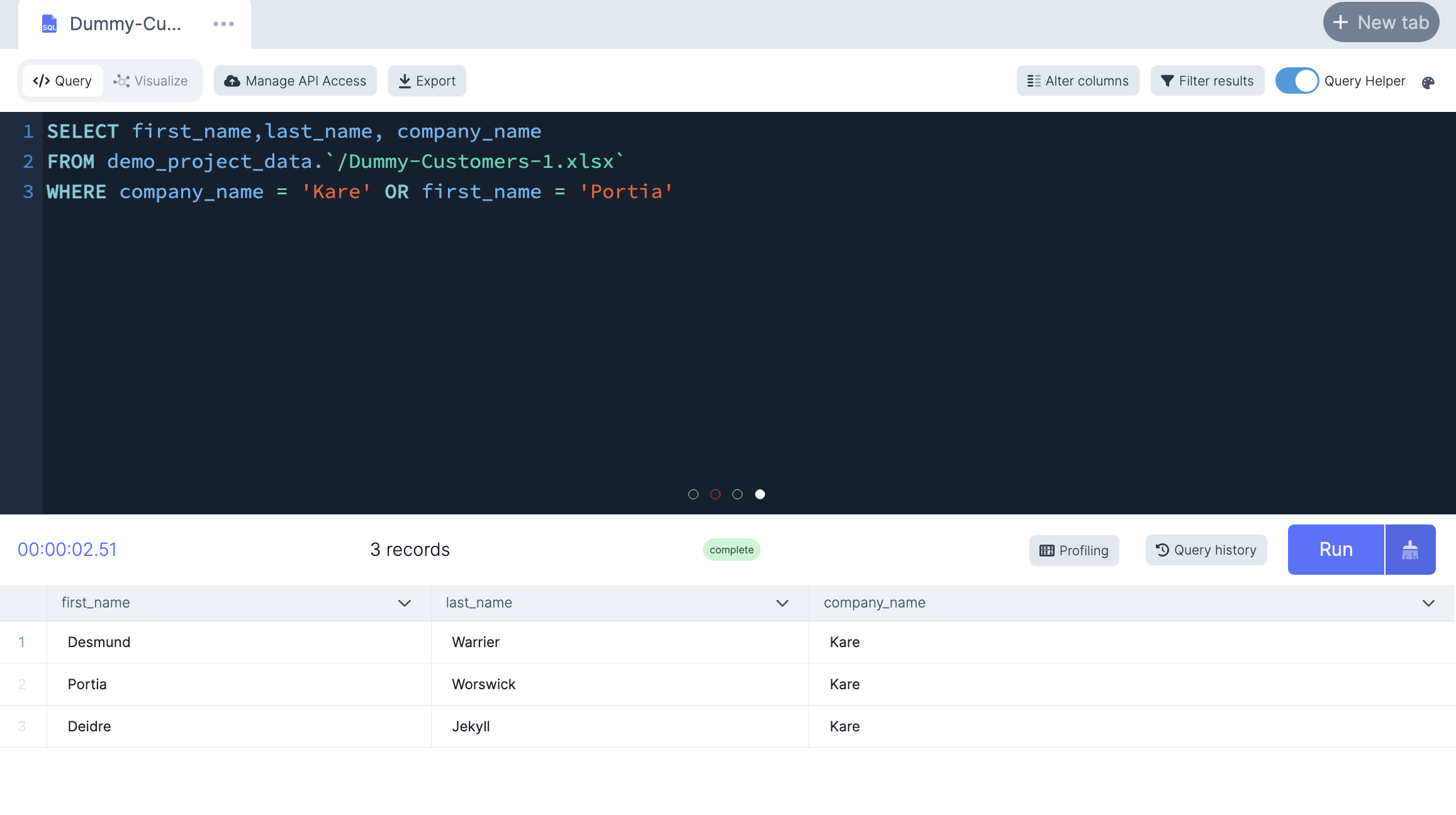
-- Only select customers from the Kare company OR whose first name is Portia
SELECT first_name,last_name, company_name
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
WHERE company_name = 'Kare' OR first_name = 'Portia'
NOT
This operator filters records based on more than one condition and displays a record if the condition(s) is NOT TRUE.
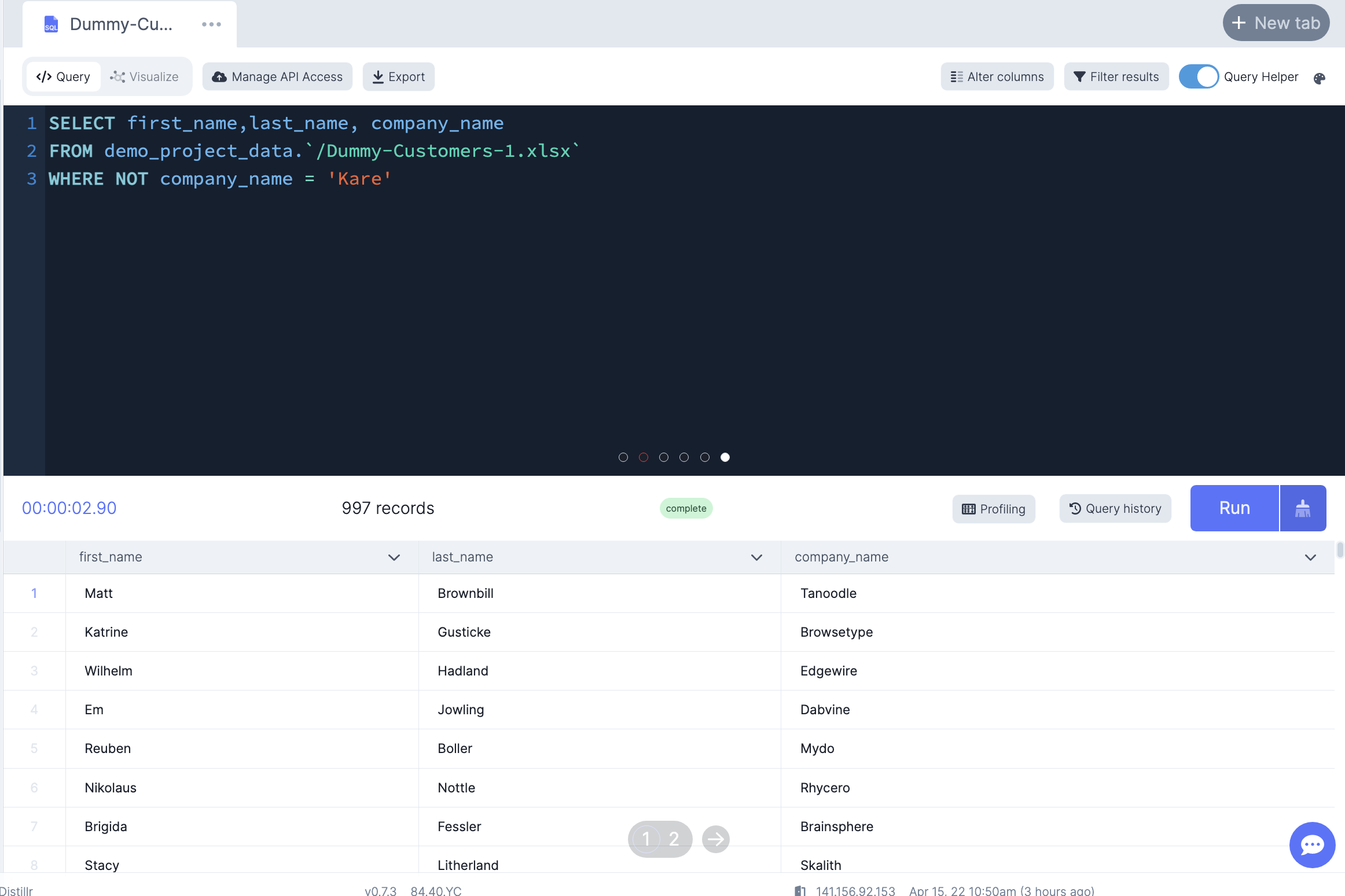
-- Only select customers who are NOT from the Kare company
SELECT first_name,last_name, company_name
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
WHERE NOT company_name = 'Kare'
IN
This operator allows you to specify multiple values in a WHERE clause and can be shorthand for multiple OR conditions.
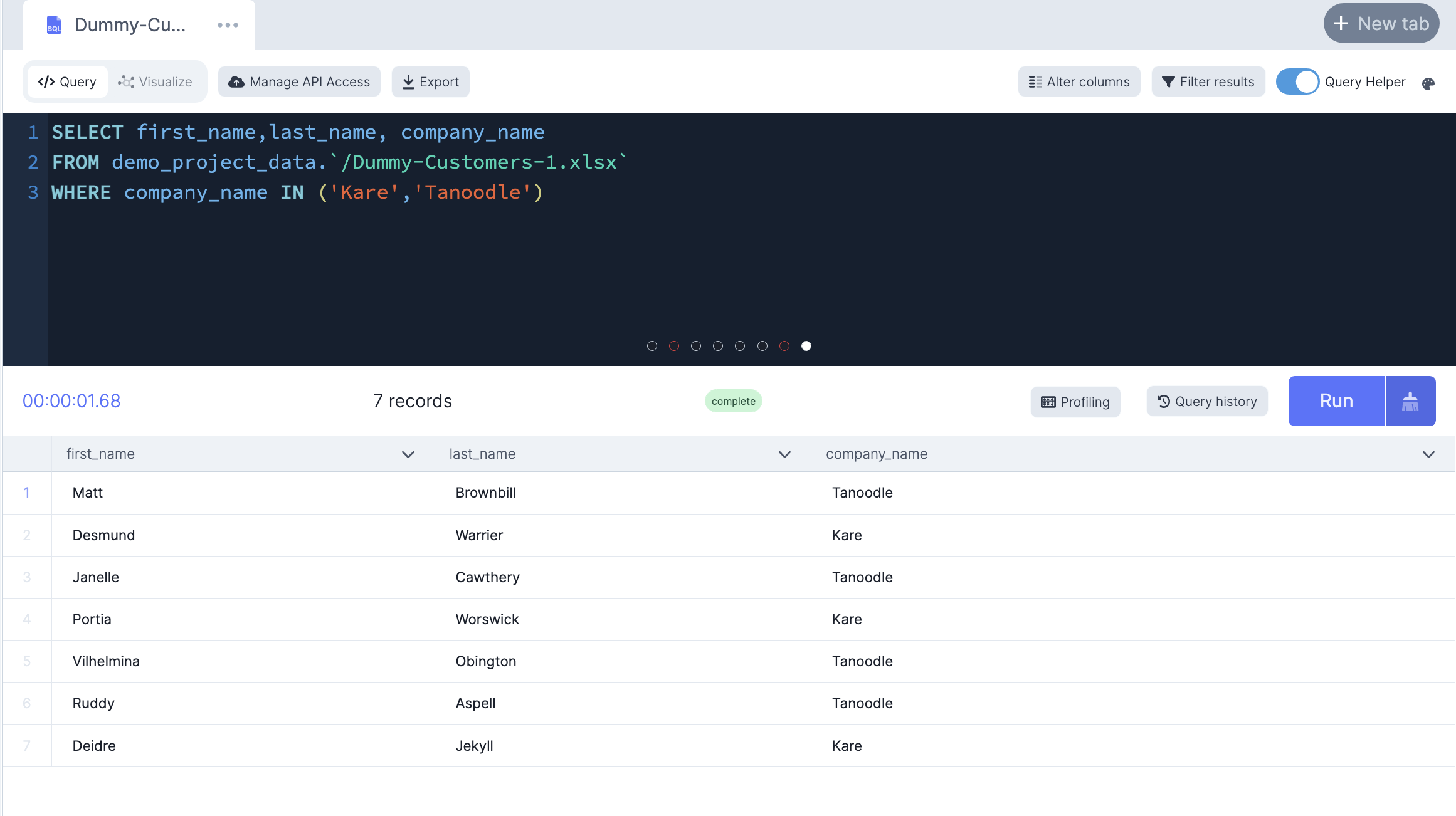
-- Only select customers from the companies Kare or Tanoodle
SELECT first_name,last_name, company_name
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
WHERE company_name IN ('Kare','Tanoodle')
BETWEEN
This operator selects values within a given range. The range is inclusive meaning the begin and end values are included. The data type can be numbers, text, or dates.
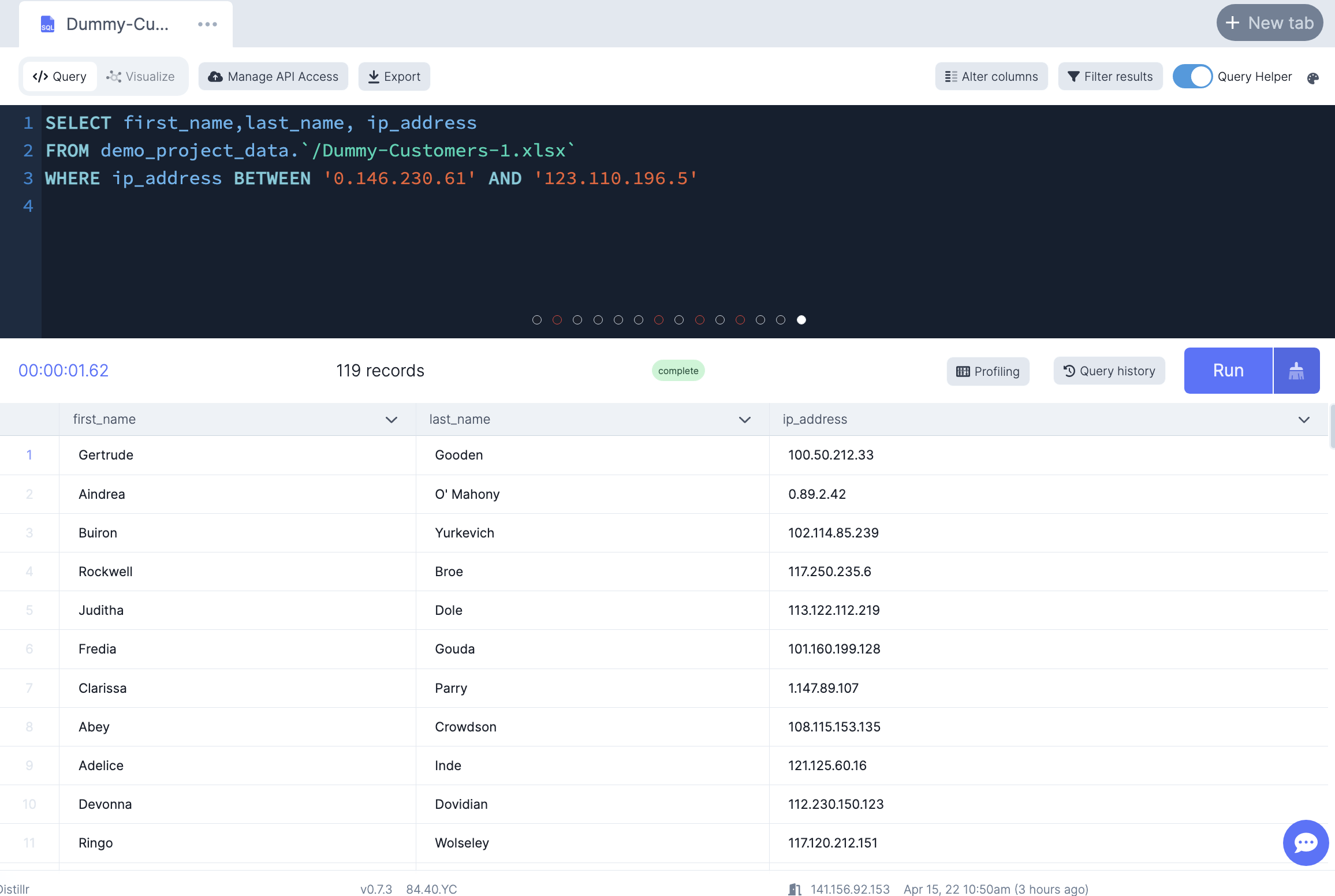
-- Select customer who's ip address are between '0.146.230.61' AND '123.110.196.5'
SELECT first_name,last_name, ip_address
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
WHERE ip_address BETWEEN '0.146.230.61' AND '123.110.196.5'
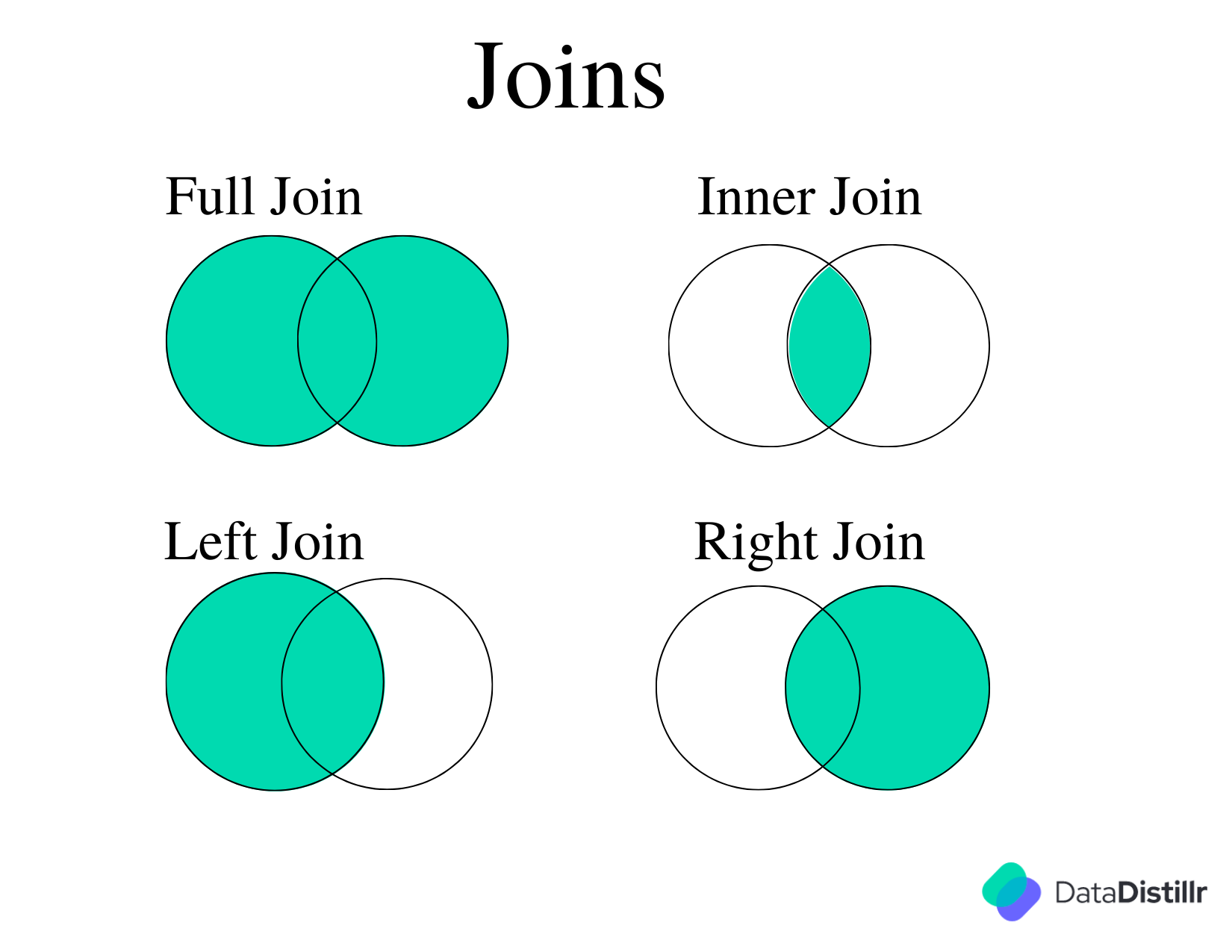
Joining Tables#
DataDistillr allows you to link different datasource on the platform. This will show you how to link tables
together using the JOIN clause which combines rows from two or more tables, based on a related column between them.
There are different types of joins in SQL:
- FULL OUTER JOIN
- INNER JOIN
- LEFT JOIN
- RIGHT JOIN
AS
This clause allows you to give a temporary name to a table or column through aliases. In the table join
examples below, we will demonstrate the following reasons why the AS clause comes in handy:
- Write clear column names for readability
- If you don't want to rewrite full column names every time you reference a column, you can rename columns to an acronym
- If you have duplicate column names across different tables, you can rename the columns to make them unique
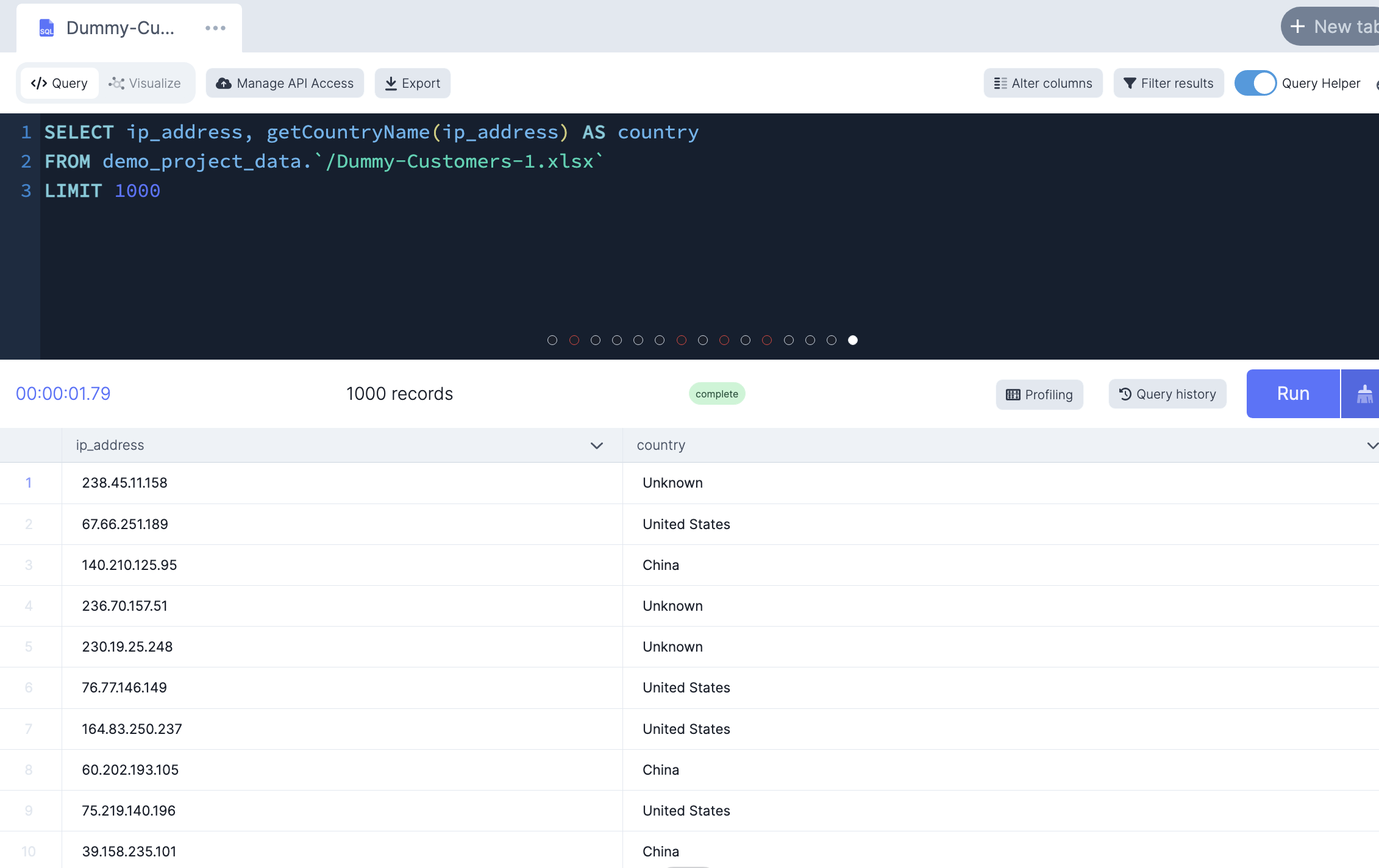
-- Rename columns for readability
SELECT ip_address, getCountryName(ip_address) AS country
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
LIMIT 1000
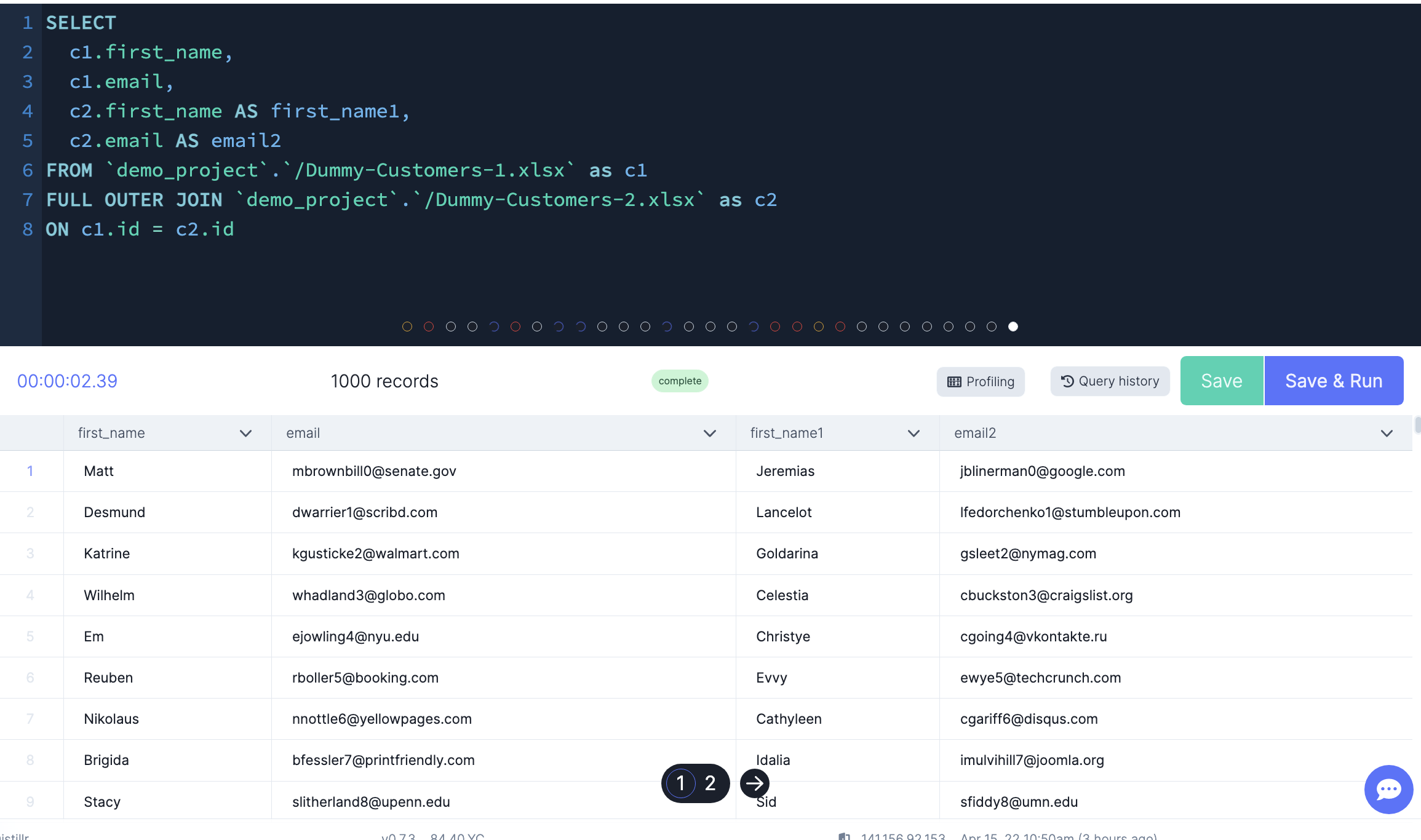
FULL OUTER JOIN
This join includes all rows from the joined tables whether or not the other table has the matching row
-- Full join of two tables based on id number, should return everything
SELECT
c1.first_name,
c1.email,
c2.first_name AS first_name1,
c2.email AS email2
FROM `demo_project`.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx` AS c1
FULL OUTER JOIN `demo_project`.`/Dummy-Customers-2.xlsx` AS c2
ON c1.id = c2.id
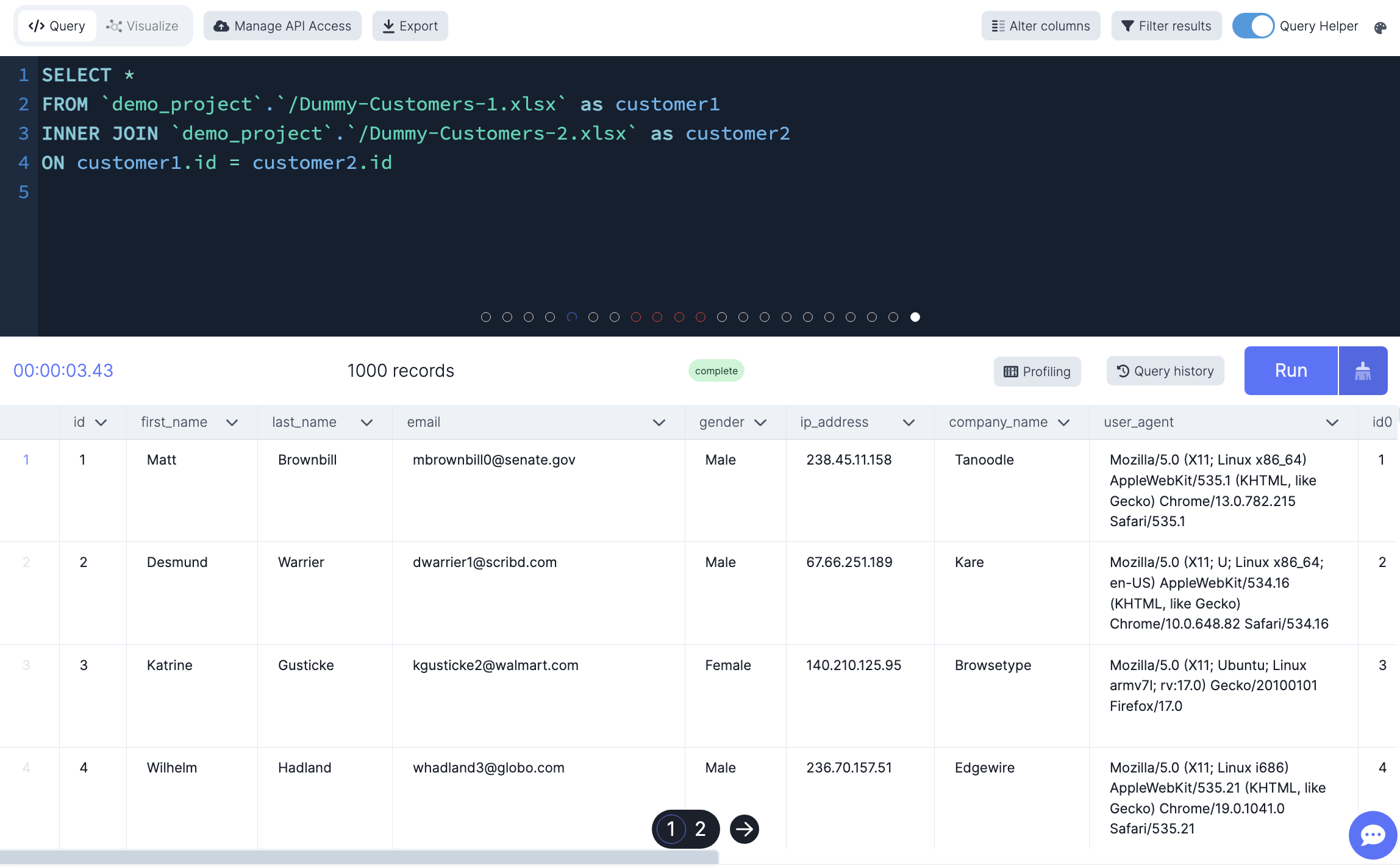
INNER JOIN
This join returns rows if there is, at least, one row in both tables that matches the join condition. This eliminates the rows that do not match with a row of the other table
For each row in column_name1, the inner join clause finds the matching rows in column_name2. If a row is matched, it is included in the final result set.
-- Inner join both tables based company name
SELECT *
FROM `demo_project`.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx` AS customer1
INNER JOIN `demo_project`.`/Dummy-Customers-2.xlsx` AS customer2
ON customer1.id = customer2.id
The query below shouldn't return anything because first names are not repeated in both tables
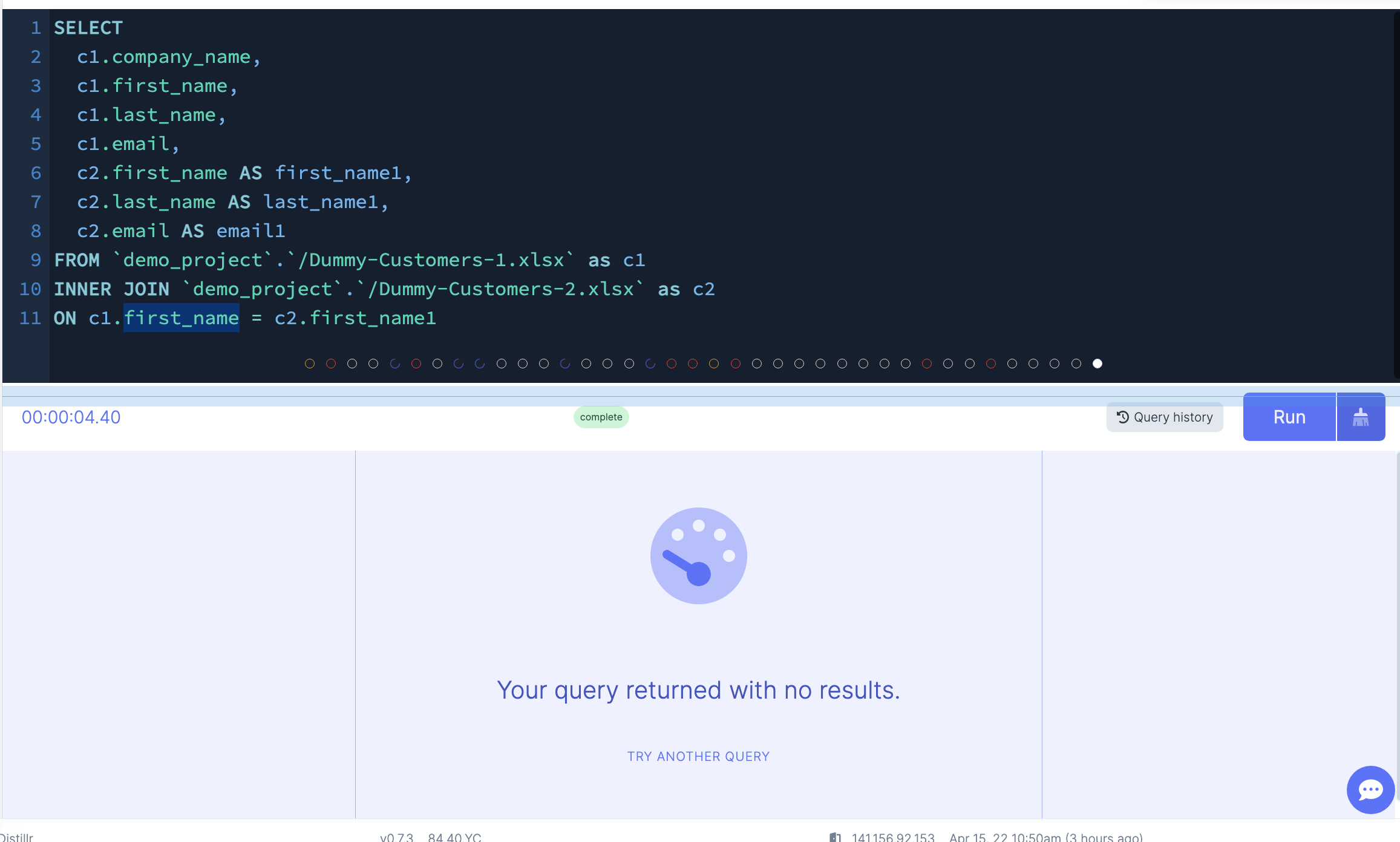
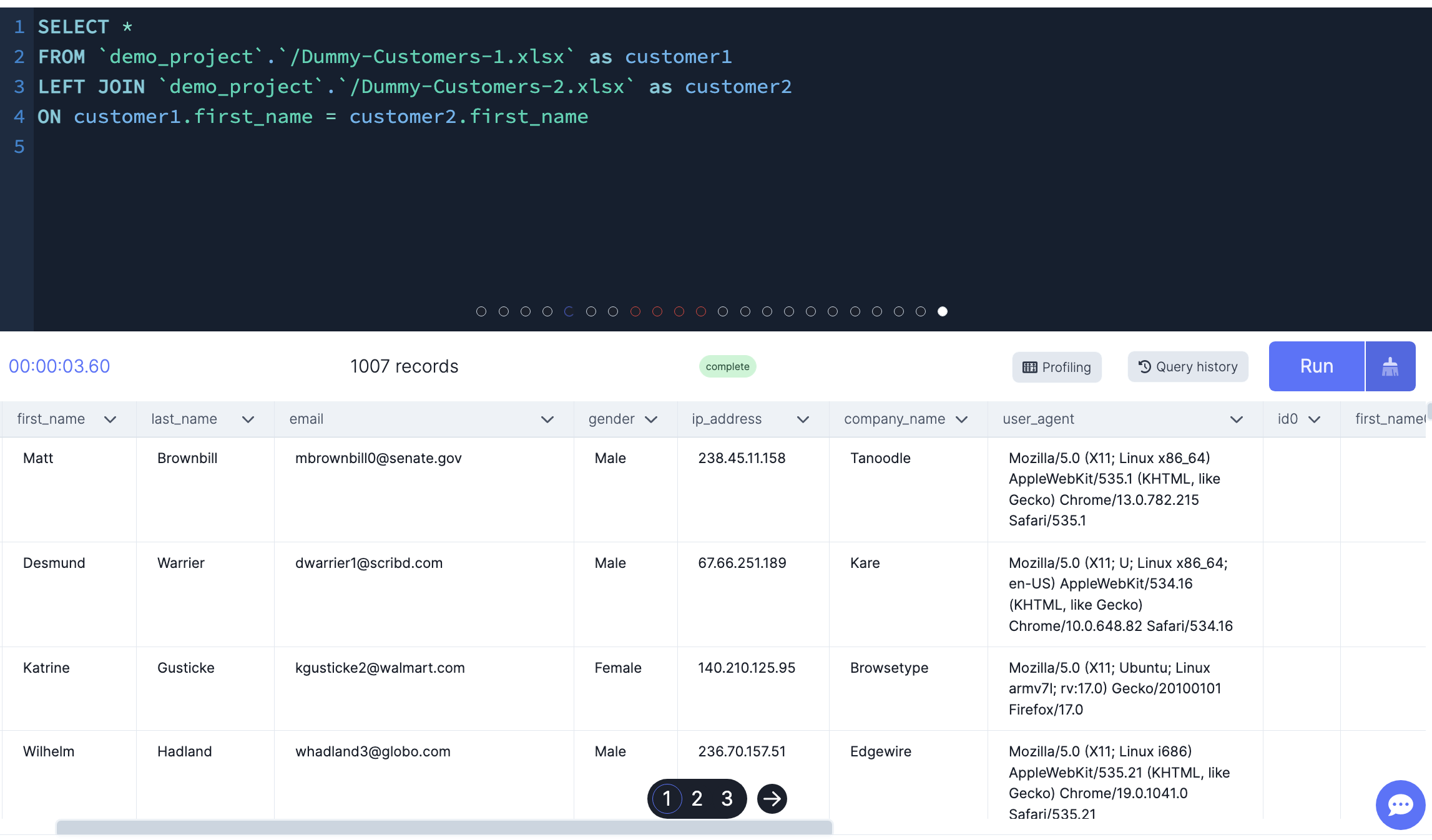
LEFT JOIN
This join returns all rows from the left table regardless of whether there is a matching row in the right table.
-- Left join tables based on the same fist name. Only 7 People have the same name.
SELECT *
FROM `demo_project`.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx` as customer1
LEFT JOIN `demo_project`.`/Dummy-Customers-2.xlsx` as customer2
ON customer1.first_name = customer2.fist_name
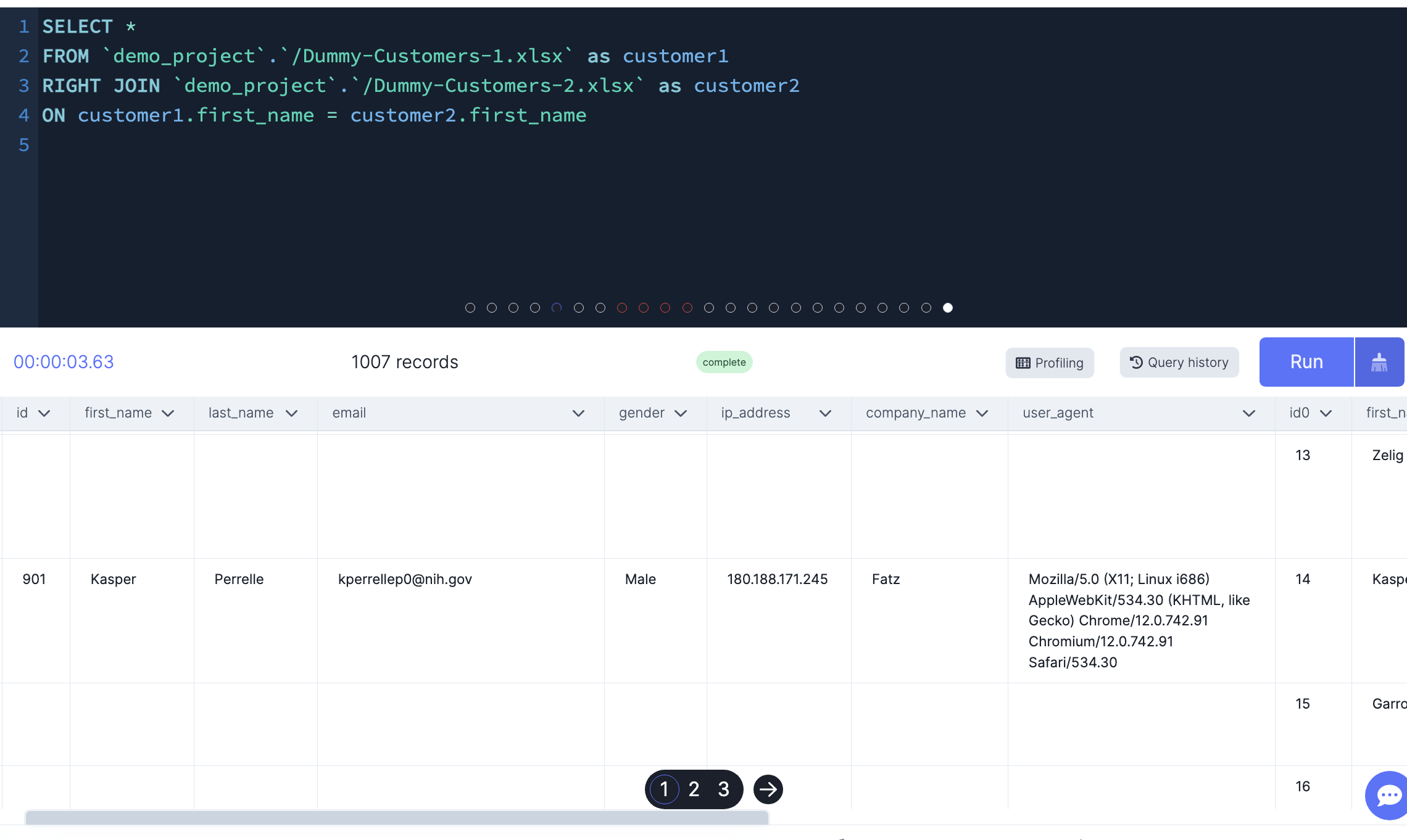
RIGHT JOIN
This clause returns all rows from the right table whether or not there is a matching row in the left table.
-- Right join based on first name. Only 7 people have the same first name
SELECT *
FROM `demo_project`.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx` as customer1
RIGHT JOIN `demo_project`.`/Dummy-Customers-2.xlsx` as customer2
ON customer1.first_name = customer2.first_name
Aggregate Functions#
SQL has built-in functions that allow you to perform basic calculations on your dataset detailed below:
- MIN()
- MAX()
- COUNT()
- AVG()
- SUM()
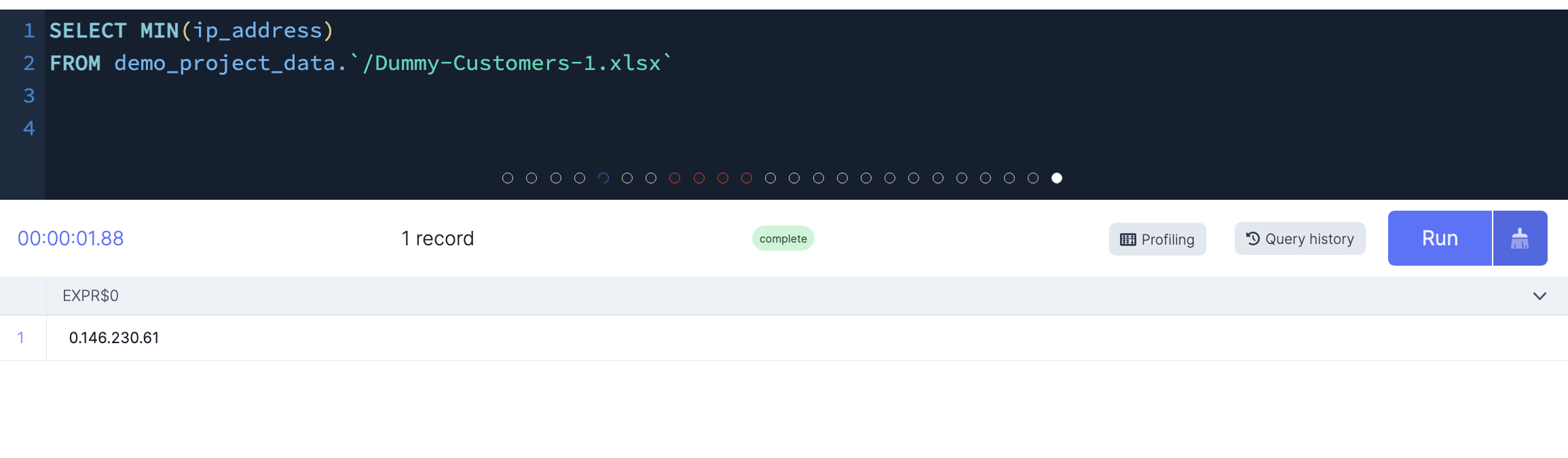
MIN()
This function returns the smallest value of the selected column.
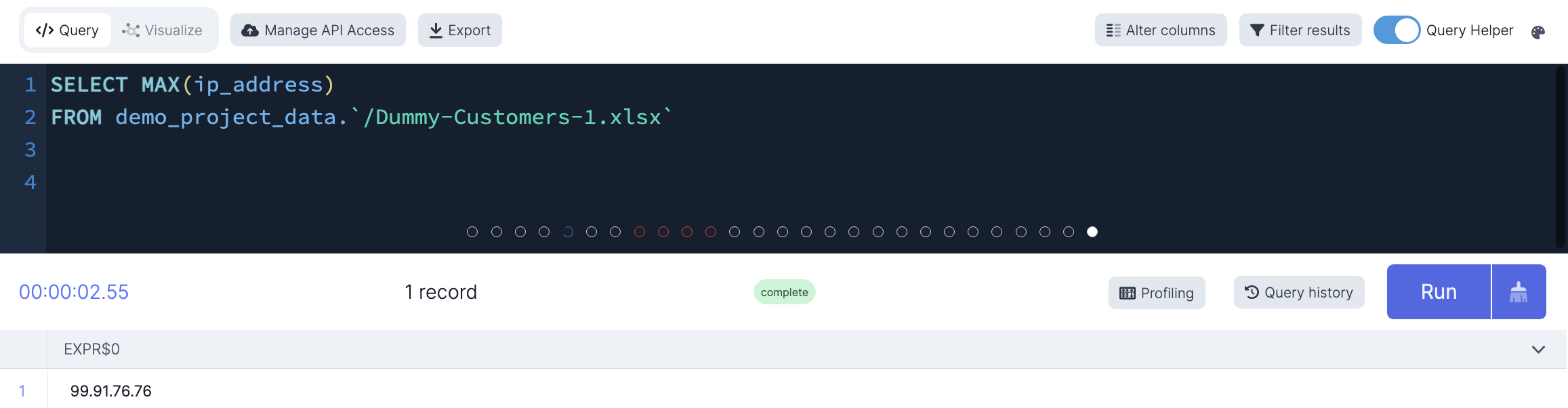
MAX()
This function returns the largest value of the selected column.
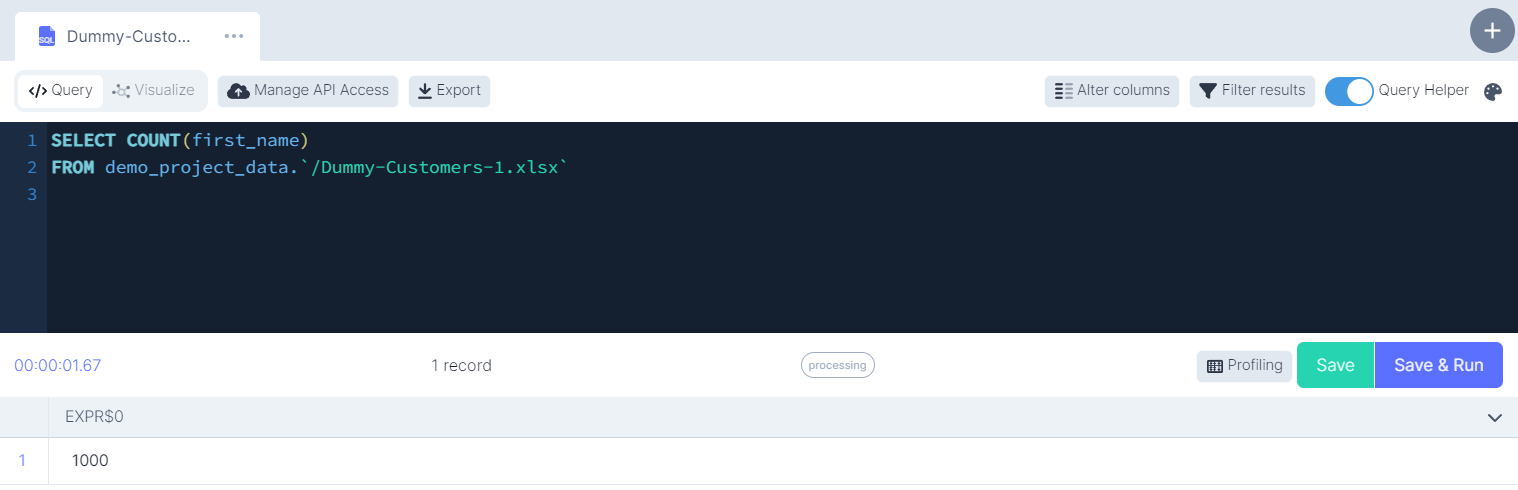
COUNT()
This function returns the number of rows that matches a specified criterion.
-- Count the number of first names in the dataset
SELECT COUNT(first_name)
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
AVG()
This function returns the average value of a numeric column. This calculates the average value of a set.
-- Calculate the average value of the column
SELECT AVG(column_name)
FROM demo_project_data.`/Dummy-Customers-1.xlsx`
SUM()
This function returns the total sum of a numeric column only. This can be distinct values or all values within the column