Connecting to Splunk#
Splunk Data Source Form#
To setup a data source connection for Splunk, you will need to have:
- A unique name for your data source connection to be used in queries
- The hostname and port for your Splunk instance
- Your access credentials
- Earliest and Latest Time boundary values
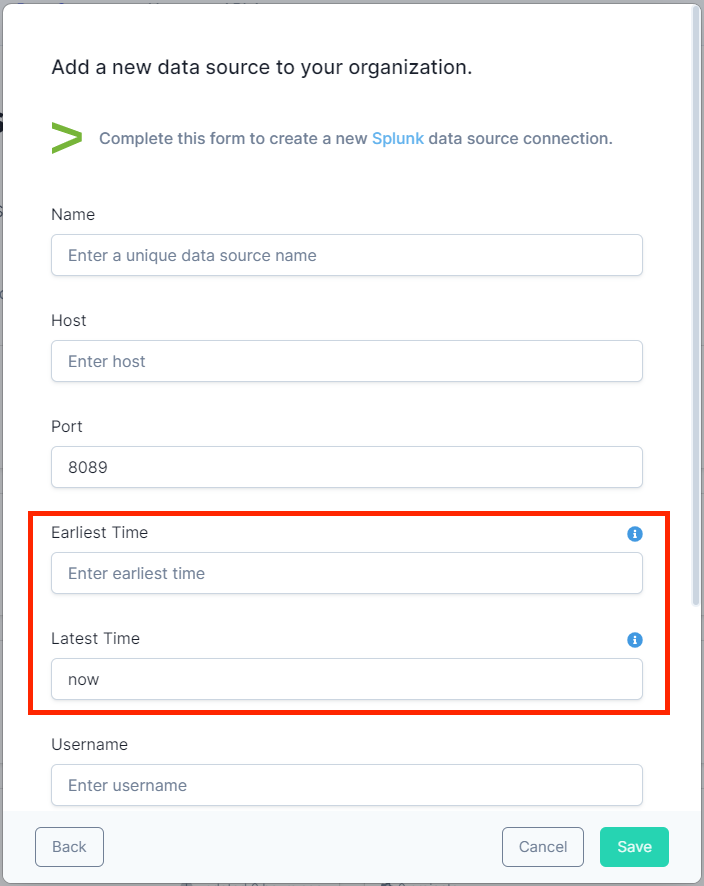
Time Boundaries#
Splunk’s primary use case is analyzing event logs with a timestamp. As such, data is indexed by the timestamp, with the most recent data indexed first. It is very important to put time boundaries on your Splunk queries so that they are looking at the shortest time span possible.
The Splunk data source form requires you to set default time boundary values in the configuration to time-bound every query you run. Alternatively, you can set the time boundaries at query time. In either case, you will achieve the best performance when you ask Splunk for the minimum amount of data.
Setting Default Boundaries in the Data Source Form#
The Splunk data source form provides fields for setting the default 'Earliest Time' and 'Latest Time' values which determine the time range of data to return. These fields accept:
- Relative time: For example, setting Earliest Time to "-60m" and Latest Time to "now" will return data from the last hour. You can use any of the relative time formats specified in the Splunk documentation.
- Absolute time: Use a Unix timestamp. For example, "1539907200" is Friday, October 19, 2018 00:00:00 GMT.
Modifying Time Boundaries in the Query#
You can modify the time boundaries at query time via special filters in the WHERE clause. There are two
fields, earliestTime and latestTime, that can be set to bound the query like the example below. If earliestTime
and latestTime are not set, the query will be bounded to the defaults set in the data source configuration.